Data collector for vSphere
- name:
- Data collector for vSphere
- description:
- Synchronize a set of vSphere CIs into iTop
- version:
- 1.4.0
- release:
- 2025-07-16
- itop-version-min:
- 3.2
- code:
- combodo-data-collector-for-vsphere
- state:
- stable
- alternate-name:
- vSphere Data Collector
- diffusion:
- iTop Hub
- php-version-max:
- 8.4
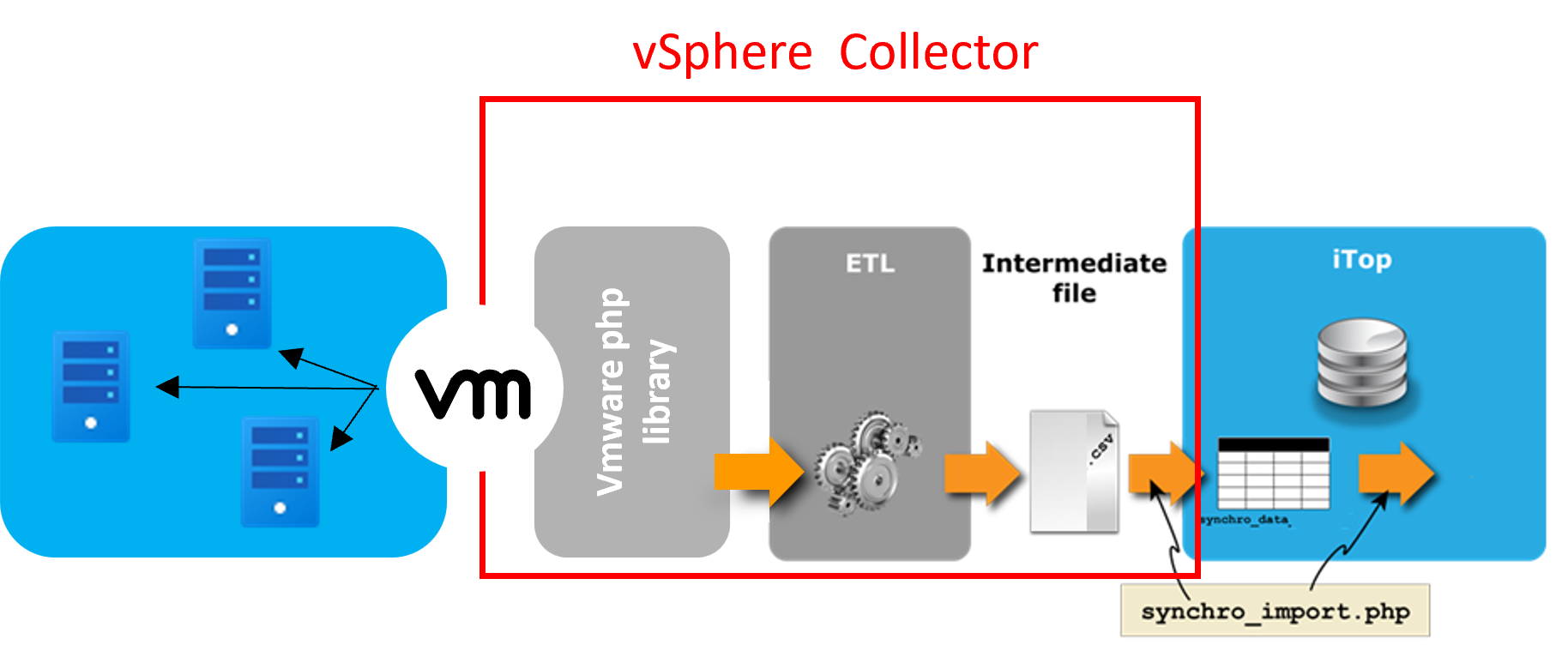
This stand-alone application collects information about a whole data center from a vSphere server and synchronizes this information in iTop.
Features
The Data collector for vSphere is a stand-alone PHP software that extracts from vSphere informations related to a set of CIs and synchronizes them with iTop's CMDB.
-
Collection of CI informations is done through a VMware / vSphere PHP library,
-
Synchronization follows iTop's built-in Data Synchronization mechanism.
The collector currently focuses on the following classes of objects, for which collection can be activated or deactivated on an individual basis:
-
Brand
-
Model
-
OS Family
-
OS Version
-
Farms
-
Server
-
Hypervisors
-
Virtual Machine
-
Logical Interface - Requires TeemIP / IPAM for iTop extension
-
IPv4 Address - Requires TeemIP / IPAM for iTop extension
-
IPv6 Address - Requires TeemIP / IPAM for iTop extension
-
Datastore - Requires iTop extension Data Model for vSphere
The collection mechanism can be extended.
Revision History
| Release Date | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 2025-07-16 | 1.4.0 | * Review and enhance initialization of collection
plan * Add power_state attribute to VMs * Use full_load_periodicity defined in conf params * N°7625 - Link between VM/ESX and datastore is not filled by vsphere collector * N°7865 - VSphere Collector - field guest OS not supported * N°6888 - [ER] VSphere collector : manage the case when we do not have access to the network components - rework * PR #10 - Use filter_var to check IPv4 and IPv6 addresses * PR #11 - Fix ipv4 address detection when TeemIp is used * PR #12 - Collection of IPs in case of TeemIP * PR #14 - Change collector submission order * PR #15 - Add and adapt interface management - PR reworked * PR #17 - Updated the library to have more error messages |
| 2024-09-10 | 1.3.0 | * N°6052 - Add compatibility with PHP 8.2-8.3 to
the VMware library * N°7267 - Typo in port detection |
| 2024-01-31 | 1.2.0 | * Allow Hypervisors and VMs collection even if
Farms are not collected * Adapt collector to different TeemIp installation options * IPv6 addresses can now be synchronized with iTop 3.1 * Fix EventIssue creation comment not interpreting variable * N°1747 - Change VM's CPU attribute to more relevant VMware source * N°5544 - Add a collection plan to the extension and adapt it to new collector base structure * N°5937 - VSphere Collector - Datastore collect * N°6044 - dump_tasks.php: Fix database_table_name option always dumped to empty string * N°6226 - Synchronization of attributes marked as “Optional” is not properly configured by collector base * N°6420 - dump_tasks.php: Improve dump log * N°6726 - Add missing default config parameters in /conf/params.distrib.xml * N°6727 - Fix config dump with special characters * N°6773 - DEBUG log of the synchro error message (Thanks Hipska !) * N°6888 - [ER] VSphere collector : manage the case when we do not have access to the network components * N°6956 - Improve CollectionPlan PHPDoc to ease DX in IDE * N°7028 - Add option to only consider the ESX as the VM's virtual host, even if the ESX belongs to a farm |
| 2023-03-10 | 1.1.0 | * Prevent a PHP Warning when there is no
custom_synchro definition * Trace the hypervisor software and API version (in DEBUG) * Accept E1000E network devices (thanks to @rudnerbjoern) * N°5067 - Cleanup RestClient::GetFullSynchroDataSource() (thanks to @Hipska) * N°5707 - Contact to notify can also be a Team (thanks to @Hipska) * N°5868 - Add PHP 8.0 / 8.1 compatibility (collector base) * N°5868 - Add PHP 8.0 / 8.1 compatibility (vSphere collector) * N°5884 - Missing attributes in aSkippedAttribute * N°5950 - cleanup code and fix some futurs bugs in php 8.2 * N°5979 - Remove PHP warning and hide test data collectors in iTop setup * N°5995 - Fix PHP warning on lookup when table is empty * N°6093 - Remove friendlyname in JSON configuration as it is no longer returned by iTop |
| 2020-12-21 | 1.0.16 | Fix compatibility with SSO set as default connection mode |
| 2020-10-20 | 1.0.14 | - Fix PHP Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Class IOException not found |
| 2020-07-07 | 1.0.13 | - Differenciates error/logs between teemip NOT
installed and itop REST API issue - Multi configuration file - New CSV collector - Configurable timestamp added in the logs - New option for usage: –help |
| 2020-04-02 | 1.0.12 | - Made the Server and Hypervisor collectors
configurable - Fix for a crash caused by a blank datastore name (thanks to David Wißen from ITOMIG for reporting it). - Fix for some OpenVM Tools reporting IP addresses with a trailing space (thanks to Martin Raenker from ITOMIG). |
| 2018-12-31 | 1.0.11 | Corrects regression introduced by 1.0.10 : - Improved support of iTop 2.4+ (obsolescence flag) - Removed a debug trace - Fix Virtual machines which “connectionState” is not “connected” are skipped |
| 2018-08-24 | 1.0.10 | Handles TeemIp : - Automatically detects if TeemIp (as an iTop module or as a standalone application) is present. - Optional synchronization of IPv4 addresses - Optional synchronisation of logical interfaces |
| 2018-07-02 | 1.0.9 | Robustness : - more traces in debug mode (–console_log_level=9) - skipping virtual machines which “connectionState” is not “connected”, since most of their properties are not accessible and would crash PHP/Soap (with a core dump !!) |
| 2018-02-22 | 1.0.8 | - The os_version_mapping was used
only for Hypervisors, made it work for VirtualMachines also.Proper support of UTF-8 characters in regular expressions (the code now always uses the u modifier) |
| 2017-04-24 | 1.0.7 | Fixed the value for the status of VMs: 'production' instead of 'active'. |
| 2017-03-08 | 1.0.6 | - Code cleanup. - Data Synchro status and
full_load_interval are now homogeneous and
configurable parameters for all data sources.- OS Version and OS Family have their own mapping table. - Fix for the Hypervisor status value (now defaults to “production”). - Addition of the check_soap.php script for
troubleshooting.- Protect against a PHP crash in case of a disconnected ESX. - Do not collect an IPV6 as the management IP address of a virtual machine (since the field can only contain an IPV4). Many thanks to Andrew Armstrong for proposing this fix. |
| 2016-12-08 | 1.0.5 | New options to bypass SSL certificate validation and automatic detection of invalid certificates. |
| 2015-11-16 | 1.0.4 | Replace line-breaks by spaces inside the description of a VM. Fix the +1 on the number of vCPUs |
| 2015-04-17 | 1.0.3 | Added the collection of the “description” field for a VM |
| 2015-02-23 | 1.0.2 | Servers must be loaded before hypervisors |
| 2015-01-07 | 1.0.1 | Beta version |
| 2014-05-13 | 1.0.0 | First alpha version |
Limitations
The vSphere collector is currently relying on the a slightly adapted version of the PHP Vmwarephp library. It supports vSphere API from version 4.1 to 7.0 but it is NOT compatible with version 8.0.
The current version of the collector is designed to collect information from a single vSphere server. To collect and reconcile information from several vSphere servers into one iTop, check the section Collecting from several vSphere servers below.
Requirements
Usage of the collector requires you to comply with a few points:
-
PHP Version 7.4.0 minimum
-
An access to the vSphere web services API (version 7 maximum)
-
An access to the iTop web services
-
The vSphere objects synchronized by the collector must exist in iTop as CMDB CIs.
-
This is the default case for most collected objects if iTop has been installed with the Virtualization Management Module,
-
Logical interfaces, IPv4 and IPv6 Addresses do need TeemIP / IPAM for iTop,
-
Datastores require iTop extension Data Model for vSphere
-
-
From a system standpoint:
-
You'll need to comply with the requirements expressed in the Data collector Base documentation.
-
PHP version should be 8.1, 8.2 or 8.3.
-
Installation
Simply expand the content of the zip archive into a folder on the machine where the collector will be run.
Configuration
The configuration of the application is built by concatenating 4 files:
-
conf/params.distrib.xml that is provided by the collector framework, Data collector Base. It should not be modified.
-
collectors/params.distrib.xml that holds the entries that are specific to the Data collector for Azure. It should not be modified.
-
collectors/extensions/params.distrib.xml that holds entries that have been created and added by the customer to answer its specific needs. This file is optional.
-
conf/params.local.xml where the collector can be adapted to the specific customer needs.
The collectors/params.distrib.xml configuration file holds parameters that must (for some) or can (for others) be changed when configuring the collector, which is done through the conf/params.local.xml file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- Default values for parameters. Do NOT alter this file, use params.local.xml instead --> <parameters> <!-- vSphere Parameters --> ... List of parameters to connect to the remote vSphere application ... <!-- Default values --> ... Default paramaters that drive the collect ... <!-- Class collection sequence --> ... List of classes to collect with the rank in the collection process ... <!-- Synchronization parameters --> ... Placeholders for the synchro data sources ... <!-- IPs and logical interfaces collection --> ... Parameters that dedicated to the collect of TeemIP objects ... <!-- Mapping tables --> ... Set of mapping tables ... </parameters>
The collectors/extensions/params.distrib.xml configuration file holds parameters to collect additional classes required by a customer.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- Default values for parameters. Do NOT alter this file, use params.local.xml instead --> <parameters> <!-- Default values --> ... List of default values for the additional classes to collect ... <!-- Class collection sequence --> ... List of additional classes to collect with the rank in the collection process ... </parameters>
Connection parameters
This set of parameters is required to connect to the iTop application or the vSphere environment. Some of them must or may be adapted to meet customers' own environment.
| Parameter | Meaning | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| itop_url | URL to the iTop Application | https://localhost/myitop |
| itop_login | Login (user account) for connecting to iTop. Must have admin rights with rest profile for executing the data synchro | admin |
| itop_password | Password for the iTop account | admin_pwd |
| itop_token | Token defined in iTop for a given user. Please, refer to the Authentication by Token extension | |
| itop_login_mode | Redefine the login_mode defined in URLs that access iTop | |
| vsphere_uri | Address/port to connect to vSphere. Format: <name>:<port> or <ip_address>:<port> | 192.168.10.12:443 |
| vsphere_login | Login to connect to vSphere | admin |
| vsphere_password | Password corresponding to the vSphere login | admin |
| vsphere_connection_options | List of PHP Stream context options to pass to the VMWarephp library in order to tune the https connection. |
params.local.xml file:
<vsphere_connection_options> <ssl> <verify_peer>0</verify_peer> <verify_peer_name>0</verify_peer_name> <allow_self_signed>1</allow_self_signed> </ssl> </vsphere_connection_options>
Default values
The section defines a set of default general parameters for the collects.
<!-- Default values --> <default_org_id>Demo</default_org_id> <hypervisor type="hash"> <!-- Define what attribute to use as cpu attribute within iTop's datamodel. numCpuPackages was used before --> <cpu_attribute>numCpuCores</cpu_attribute> </hypervisor> <virtual_machine type="hash"> <!-- By default, a VM's virtual host points to the farm that the VM's hypervisor belongs to, if any. This option forces the VM's virtual host to point to the VM's hypervisor Allowed values: hypervisor, farm (default) --> <virtual_host>farm</virtual_host> <get_network_interfaces_from_hardware_info>yes</get_network_interfaces_from_hardware_info> <get_network_interfaces_from_network_info>yes</get_network_interfaces_from_network_info> <default_interface_network_name>Internal</default_interface_network_name> <record_interface_number>yes</record_interface_number> </virtual_machine>
| Parameter | Meaning | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| default_org_id | Name of the organization that the vSphere objects belong to | Demo |
| cpu_attribute | vSphere attribute to use for the iTop cpu attribute of a VM | numCpuCores / numCpuPackages |
| virtual_host | Lock the VM's virtual host to its hypervisor or allow it to be a farm, if any | farm / hypervisor |
| get_network_interfaces_from_hardware_info | Enable the legacy method to collect interfaces, based on the scan of hw devices attached to VMs | yes |
| get_network_interfaces_from_network_info | Enable the new method to collect interfaces, based on the scan of network information attached to VMs | yes |
| default_interface_network_name | Default name given to interfaces when the collected names are empty | Internal |
| record_interface_number* | Number added to name of VMs' interfaces | yes |
Class collection sequence
This section defines the list of classes that will be collected and in which order. It enables as well the possibility to deactivate the collection of a class.
<collectors_launch_sequence type="array"> <!-- Brands --> <collector> <name>vSphereBrandCollector</name> <enable>yes</enable> <rank>1</rank> </collector> <!-- Models --> <collector> <name>vSphereModelCollector</name> <enable>yes</enable> <rank>2</rank> </collector> <!-- OS Families --> <collector> <name>vSphereOSFamilyCollector</name> <enable>yes</enable> <rank>3</rank> </collector> <!-- OS Versions --> <collector> <name>vSphereOSVersionCollector</name> <enable>yes</enable> <rank>4</rank> </collector> <!-- Farms --> <collector> <name>vSphereFarmCollector</name> <enable>yes</enable> <rank>10</rank> </collector> ... </collectors_launch_sequence>
| Parameter | Meaning | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| name | Name of the vSphere class collector | vSphereVirtualMachineCollector |
| enable | Enable or disable its collect | yes / no |
| rank | Relative rank in the collection | 30 |
IPs and logical interfaces collection
The collector automatically detects if TeemIp is present on the remote iTop application (as a module or even as a stand-alone application). Should that be the case, then the following parameters may trigger IP addresses and logical interfaces collection.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <parameters> ... <teemip_discovery type="hash"> <enable>yes</enable> <collect_ips>yes</collect_ips> <default_ip_status>allocated</default_ip_status> <manage_ipv6>yes</manage_ipv6> <manage_logical_interfaces>yes</manage_logical_interfaces> </teemip_discovery> ... </parameters>
| Parameter | Meaning | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| enable | Enable TeemIp related synchronizations | yes |
| collect_ips | Triggers IP addresses collection | yes |
| default_ip_status | Status of newly created IP addresses | allocated |
| manage_ipv6 | Triggers IPv6 collection | no |
| manage_logical_interfaces | Triggers logical interfaces collection as well as the addresses / interfaces links | yes |
Synchro data source parameters
These are dedicated to the synchronization data sources that the collector creates. Some of them must or may be adapted to meet customers' own environment.
| Parameter | Meaning | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| contact_to_notify | The email address of an existing contact (person or team) in iTop to be notified of the results of the synchronization. | it.support@demo.com |
| synchro_user | If the user account used for running this synchronization is not an Administrator, then its login must be specified here, since iTop allows only the administrators and the specified user to run the synchronization. | |
| prefix | String used to prefix the name of all vSphere synchro data sources | vSphere |
| full_load_interval | The delay (expressed in seconds) between two complete imports of the data. The objects which have not been detected by the collector during a timespan longer than this interval will be considered as obsolete and marked as such in iTop. Adjust this value depending on the scheduling recurrence. | 604800 |
| synchro_status | Default status for the synchro data source | production |
Mapping tables
This section groups the mapping tables used by the collector.
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| brand_mapping | Mapping table for brands |
| model_mapping | Mapping table for models |
| os_family_mapping | Mapping table for the OS Family |
| os_version_mapping | Mapping table for the OS Version |
| vm_power_state_mapping | Mapping table for the VMs' power state |
Should you require further details on how mapping tables should be built and use, please refer to the Data mapping chapter of the Data collector Base documentation.
Configurable collectors
Starting with version 1.0.12 of the application, Server and Hypervisor collectors are configurable by adding extra definitions in the XML parameter file.
This configuration contains two parts:
-
The first part (under the
<json>tag) allows to alter the definition of the Synchro Data Source (normally fixed by the .json file associated with the collector class). This is useful to synchronise a new field which was not synchronized by default, or to change a reconciliation rule on a field, etc… Any field under theattribute_listpart of the JSON file can be modified by specifying a new value in the configuration. -
The second part (the
<source>tag) defines the way to collect the data for the attribute. This tag must contain a (partial) PHP expression relative to the Hypervisor object (which is actually a HostSystem in the vSphere model)
Both parts of the configuration can be used independently (one can alter only the JSON or only the collection, or both).
The example below configures the collection of the “Serial
Number” on Servers (from the
otherIdentifyingInfo[EnclosureSerialNumberTag]) and
also uses the collected serial number as the reconciliation key
between Hypervisors and physical Servers (the
field server_id).
- config.local.xml
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <parameters> ... <custom_synchro> <vSphereHypervisorCollector> <fields> <server_id> <source>hardware->systemInfo->otherIdentifyingInfo[EnclosureSerialNumberTag]</source> <json> <reconciliation_attcode>serialnumber</reconciliation_attcode> </json> </server_id> </fields> </vSphereHypervisorCollector> <vSphereServerCollector> <fields> <serialnumber> <source>hardware->systemInfo->otherIdentifyingInfo[EnclosureSerialNumberTag]</source> </serialnumber> </fields> </vSphereServerCollector> </custom_synchro> ... </parameters>
<source> tag is currently only
supported on the otherIdentifyingInfo property.Usage
The launch of the vSphere collector will be driven by the command and parameters defined in the usage section of iTop Data collector base. Once launched, first action of the collector will be to define its collection plan, based on the list of classes that have been enabled in the configuration file. Then:
-
Configuration files will be consolidated,
-
Synchronisation data sources will be created or updated if required,
-
Collection of vSphere classes will be made and extracted data will be stored under the local “data” directory, in CSV format,
-
vSphere objects will be uploaded into iTop,
-
Synchronisation of the collected data with the existing iTop CIs will be made.
Servers and Hypervisors
In the vSphere web services SDK, Hypervisors and physical Servers are represented by the same object HostSystem.
The information from the vSphere HostSystem object is imported in iTop into the Server object using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| name | HostSystem → name |
| org_id | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| brand_id | The information from HostSystem → hardware →
systemInfo → vendor is processed through the mapping table
named brand_mapping |
| model_id | The information from HostSystem → hardware →
systemInfo → model is processed through the mapping table
named model_mapping |
| cpu | HostSystem → hardware → cpuInfo →
<cpu_attribute> cpu_attribute being defined in the
default configuration parameters |
| ram | HostSystem → hardware → memorySize
divided by (1024*1024) |
| osfamily_id | The information from HostSystem → config →
product → name is processed through the mapping table named
os_family_mapping |
| osversion_id | The information from HostSystem → config →
product → fullName is processed through the mapping table
named os_version_mapping |
| status | Constant value: active |
| If extension Data model for vSphere IS used | |
| hostid | vSphere reference ID |
| If TeemIp is NOT used | |
| managementip | HostSystem → name if name corresponds
to an IP |
| If TeemIp IS used and if IPs are collected | |
| managementip_id | Foreign key to an IPAddress object with ip set to
HostSystem → name if name corresponds to an IP |
The information from the vSphere HostSystem object is imported in iTop into the Hypervisor object using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| name | HostSystem → name |
| org_id | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| server_id | HostSystem → name |
| If extension Data model for vSphere IS used | |
| uuid | HostSystem → hardware → systemInfo →
uuid |
| hostid | vSphere reference ID |
| local_datastores_list | Datastores located on the server hosting the hypervisor |
| remote_datastores_list | Datastores located remotely across the network |
otherIdentifyingInfo seem to depend on
the hardware manufacturer and/or the version of the hypervisor.
Test on your systems before putting such a modification in
production.Farms
In the vSphere web services SDK, a Farm is represented by the object ClusterComputeResource.
The information from the vSphere ClusterComputeResource object is imported in iTop into the Farm object using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| name | ClusterComputeResource → name |
| org_id | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| If extension Data model for vSphere is used | |
| remote_datastores_list | Datastores located remotely across the network |
The list of hypervisors belonging to a farm is collected via the property: ClusterComputeResource → host → name.
Virtual Machines
In the vSphere web services SDK, a Virtual Machine is represented by the object VirtualMachine. The information from the vSphere VirtualMachine object is imported in iTop into the VirtualMachine object using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| name | VirtualMachine → name |
| org_id | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| description | VirtualMachine → config →
annotation |
| cpu | VirtualMachine → config → hardware →
numCPU |
| ram | VirtualMachine → config → hardware →
memoryMB |
| virtualhost_id | either the Farm (if not empty) or
VirtualMachine → runtime → host → name |
| If extension Data model for vSphere is used | |
| uuid | VirtualMachine → config → uuid |
| power_state | VirtualMachine → runtime →
powerState |
| datastores_list | Datastores used by the virtual machine |
| If TeemIp is NOT used | |
| managementip | VirtualMachine → guest →
ipAddress |
| If TeemIp IS used and if IPs are collected | |
| managementip_id | Foreign key to an IPAddress object with ip set to
VirtualMachine → guest → ipAddress |
IPv4 & IPv6 Addresses
If enabled (TeemIp / IPAM for iTop required), the information from the vSphere IPv4 and IPv6 addresses is imported in iTop into the IPv4Address or IPv6Address objects using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| org_id | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| status | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| short_name | VirtualMachine → guest →
hostName |
| ip | Virtual Machine: VirtualMachine → guest →
ipAddressHypervisor: HostSystem → name |
Regular expressions are used to discriminate between the two IP formats.
Logical Interfaces
If enabled (TeemIp / IPAM for iTop required), the collector may register the logical interfaces attached to virtual machines. These are imported in iTop into the LogicalInterface objects using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| macaddress | VirtualMachine → guest → net →
macAddress |
| name | VirtualMachine → config → hardware → device
→ backing →* network → name or* opaqueNetworkId or* deviceName or* port |
| virtualmachine_id | VirtualMachine → name |
| ip_list | List of IP addresses attached to the interface |
Datastores
In the vSphere web services SDK, a Datastore is represented by the object Datastore. If enabled (Data model for vSphere extension required), the information from the vSphere Datastore object is imported in iTop into the Datastore object using the following mapping:
| Field in iTop | Source in vSphere |
|---|---|
| name | Datastore → name |
| uuid | vSphere reference ID |
| org_id | Constant value, supplied by the configuration file |
| type | Datastore → summary → type |
| capacity | Datastore → summary → capacity
(divided by 1G) |
| status | production |
| mountingpoint | Datastore → summary → url |
| virtualmachines_list | List of all virtual machines using the datastore |
Troubleshooting
If you have troubles connecting to the vSphere server, try the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Check that the connection from the system running PHP to the vSphere server is currently possible. Use a command line tool like
wgetto connect to the vSphere server. For example if yourvsphere_uriis192.168.10.12:443, try:wget --no-check-certificate -O - https://192.168.10.12:443
If the connection does not succeed, there may be a firewall blocking your requests, or that vSphere is configured to operate on a different port (for example
9443)… ask your IT department about it. -
Once the connection seems to go fine, configure the proper
vsphere_urivalue inconf/params.local.xmland, from the command line (in thecollectorssubdirectory) launch:php check_soap.php
The expected output (with
vsphere_uri=192.168.10.12:443) is:Connecting to https://192.168.10.12:443/sdk Ok, the response looks like a valid SOAP response. --------------------- DEBUG ---------------- The request returned: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenc="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <soapenv:Body> <RetrieveServiceContentResponse xmlns="urn:vim25"><returnval><rootFolder type="Folder">group-d1</rootFolder><propertyCollector type="PropertyCollector">propertyCollector</propertyCollector><viewManager type="ViewManager">ViewManager</viewManager><about><name>VMware vCenter Server</name><fullName>VMware vCenter Server 4.1.0 build-345043</fullName><vendor>VMware, Inc.</vendor><version>4.1.0</version><build>345043</build><localeVersion>INTL</localeVersion><localeBuild>0</localeBuild><osType>win32-x86</osType><productLineId>vpx</productLineId><apiType>VirtualCenter</apiType><apiVersion>4.1</apiVersion></about><setting type="OptionManager">VpxSettings</setting><userDirectory type="UserDirectory">UserDirectory</userDirectory><sessionManager type="SessionManager">SessionManager</sessionManager><authorizationManager type="AuthorizationManager">AuthorizationManager</authorizationManager><perfManager type="PerformanceManager">PerfMgr</perfManager><scheduledTaskManager type="ScheduledTaskManager">ScheduledTaskManager</scheduledTaskManager><alarmManager type="AlarmManager">AlarmManager</alarmManager><eventManager type="EventManager">EventManager</eventManager><taskManager type="TaskManager">TaskManager</taskManager><extensionManager type="ExtensionManager">ExtensionManager</extensionManager><customizationSpecManager type="CustomizationSpecManager">CustomizationSpecManager</customizationSpecManager><customFieldsManager type="CustomFieldsManager">CustomFieldsManager</customFieldsManager><diagnosticManager type="DiagnosticManager">DiagMgr</diagnosticManager><licenseManager type="LicenseManager">LicenseManager</licenseManager><searchIndex type="SearchIndex">SearchIndex</searchIndex><fileManager type="FileManager">FileManager</fileManager><virtualDiskManager type="VirtualDiskManager">VirtualDiskManager</virtualDiskManager></returnval></RetrieveServiceContentResponse> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope> ---------------------------------------------
If the result is not the expected one, check that your vSphere server is properly configured to run as HTTPS (which should be the default).
Questions & Answers
Question: how can I add vSphere classes to the
collection plan ?
Answer: Other classes than the ones listed by default in the
collector can be added to it. For that purpose, we highly recommend
to use the extensibility mechanism that is available since version
2 of the collector (version 1.3.0 of iTop Data Collector Base).
-
Make sure the class (MyNewClass) has been modelized in iTop (Through the Data model for vSphere extension for instance).
-
Within the <your_collector>/collectors/extensions/ directory:
-
Create a params.distrib.xml file
-
Add default parameter for MyNewClass, if needed,
-
Add a extensions_collectors_launch_sequence similarly to what is done in the Class Collection Sequence section,
-
-
Create the json/MyNewClassvSphereCollector.json file that describes the synchro data source of the new class,
-
Create the src/MyNewClassvSphereCollector.class.inc.php file that contains the collector specificities for the class,
-
-
And that's it 🙂
You may refer to what already exists for other classes as examples.
Question: can I connect the collector to a VMware
vSphere platform managed by OVHcloud ?
Answer: Unfortunately not. It looks like OVH is blocking the
URL used by the
vmwarephp library to access vSphere resources. You may refer to
this post on SourceForge for further details.